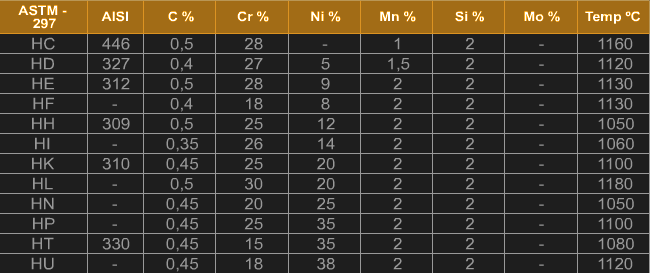
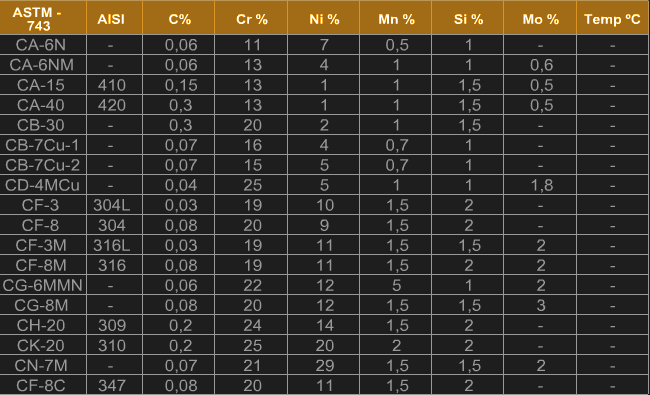
Martensitic
The martensitic stainless steels are alloys Fe-Cr-C, which in hard conditions, process a martensitic crystalline structure. They are ferromagnetic, heat-treatable, and corrosion-resistant only in medium-aggressive media. Chromium content is generally between 10.5 and 18%, and carbon content cannot be higher than 1.2%. The carbon and chromium contents are balanced to ensure a martensitic structure. Some elements such as niobium, silicon, tungsten, and vanadium are sometimes added to modify the behavior of steel during tempering. Small amounts of nickel may be added to improve corrosion resistance. Similarly, sulfur and selenium can be added to improve machinability.
Application
These steels are specified when an application requires high tensile, creep, and fatigue strength combined with moderate corrosion resistance requirements and uses up to 650 °C. Its applications include steam turbines, jet engines, and gas turbines. Some of these steels also find applications, such as steam pipes, steam generator reheaters and overheated pipes used in fossil fuel refineries, cutlery, valve parts, gears, shafts, rolling cylinders, surgical and dental instruments, springs, cams, and ball bearings.